math(M)
math --
math functions and constants
Syntax
#include <math.h>
Description
This file contains declarations of all the functions in the
Math Library (described in Section 3M),
as well as various functions in the C Library (Section 3C)
that return double, float and long double-precision values.
It defines the structure and constants used by the
matherr(S)
error-handling mechanisms, including
the following constant used as an
error-return value:
HUGE-
The maximum value of a single-precision floating-point number.
The following mathematical constants are defined for user convenience:
M_E-
The base of natural logarithms
(e).
M_LOG2E-
The base-2 logarithm of
e.
M_LOG10E-
The base-10 logarithm of
e.
M_LN2-
The natural logarithm of 2.
M_LN10-
The natural logarithm of 10.
M_PI-
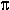 , the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
M_PI_2-
 /2.
/2.
M_PI_4-
 /4.
/4.
M_1_PI-
1/
 .
.
M_2_PI-
2/
 .
.
M_2_SQRTPI-
2/
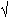
 .
.
M_SQRT2-
The positive square root of 2.
M_SQRT1_2-
The positive square root of 1/2.
The numerical classification constants are defined in this header file:
FP_INFINITE-
FP_NAN-
FP_NORMAL-
FP_SUBNORMAL-
FP_ZERO-
represent the mutually exclusive kinds of possible floating-point values.
They expand to integer constant expressions with distinct values.
The following fma performance indicator constants are defined
in this header file:
FP_FAST_FMA-
If defined, FP_FAST_FMA indicates that
fma(S)
generally executes about as fast as, or faster than
a multiply and an add of double operands.
FP_FAST_FMAF-
If defined, FP_FAST_FMF indicates that
fmaf(S)
generally executes about as fast as, or faster than
a multiply and an add of float operands.
FP_FAST_FMAL-
If defined, FP_FAST_FMAL indicates that
fmal(S)
generally executes about as fast as, or faster than
a multiply and an add of long double operands.
NOTE:
Typically, these constants are only defined if the fma
functions are implemented directly with a hardware
multiply-add instruction.
The following ilogb constants are defined
in this header file:
FP_ILOGB0-
Is set to either INT_MIN or -INT_MAX when
ilogb(S)
is called with its argument set to zero.
FP_ILOGBNAN-
Is set to either INT_MAX or INT_MIN when
ilogb(S)
is called with its argument set to NaN.
The following integer constants used by
math_errhandling are defined in this header file:
MATH_ERRNO-
Expands to 1.
MATH_ERREXCEPT-
Expands to 2.
The following mathematical constants are also defined in this header file:
MAXFLOAT-
The maximum value of a non-infinite single-precision floating point number.
HUGE_VAL-
A double constant expression representing positive infinity.
HUGE_VALF-
A float constant expression representing positive infinity.
HUGE_VALL-
A long double constant expression representing positive infinity.
The following constant is only defined on machines that support quiet
NaNs for the float type:
NAN-
A float constant expression representing a quiet NaN.
For the definitions of various machine-dependent constants,
see
values(M).
See also
matherr(S),
fma(S),
fmaf(S),
fmal(S),
ilogb(S),
values(M)
Standards conformance
math is conformant with:
ISO/IEC 9945 1:1990, Information technology
1:1990, Information technology  Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX)
Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX)  Part 1: System Application Program Interface (API) [C Language] (IEEE Std 1003.1
Part 1: System Application Program Interface (API) [C Language] (IEEE Std 1003.1 1990);
1990);
X/Open CAE Specification, System Interfaces and Headers, Issue 4, 1992.
© 2003 Caldera International, Inc. All rights reserved.
SCO OpenServer Release 5.0.7 -- 11 February 2003
 , the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
 /2.
/2.
 /4.
/4.
 .
.
 .
.
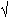
 .
.
 , the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
 /2.
/2.
 /4.
/4.
 .
.
 .
.
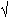
 .
.
 1:1990, Information technology
1:1990, Information technology  Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX)
Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX)  Part 1: System Application Program Interface (API) [C Language] (IEEE Std 1003.1
Part 1: System Application Program Interface (API) [C Language] (IEEE Std 1003.1 1990);
1990);